|
华为智能高频开关电源华为智能高频开关电源华为高频开关电源,华为开关电源 随着消费者对更多内容、更高视频体验的诉求提升,视频节目信号UHD化引起速率升级,从而带动媒资专线的升级换代。媒资专线作为视频产业基础设施,潜在高价值客户分布广泛,是运营商的新蓝海市场。 从摄像机到屏幕的视音频信号传播之旅 2018年的俄罗斯世界杯足球赛事,给全球广大球迷带来了一场视觉盛宴。以本届世界杯赛事的俄罗斯本地转播为例,我们来了解从摄像机镜头素材采集到最终用户屏幕视音频信号需要经历的分发过程。
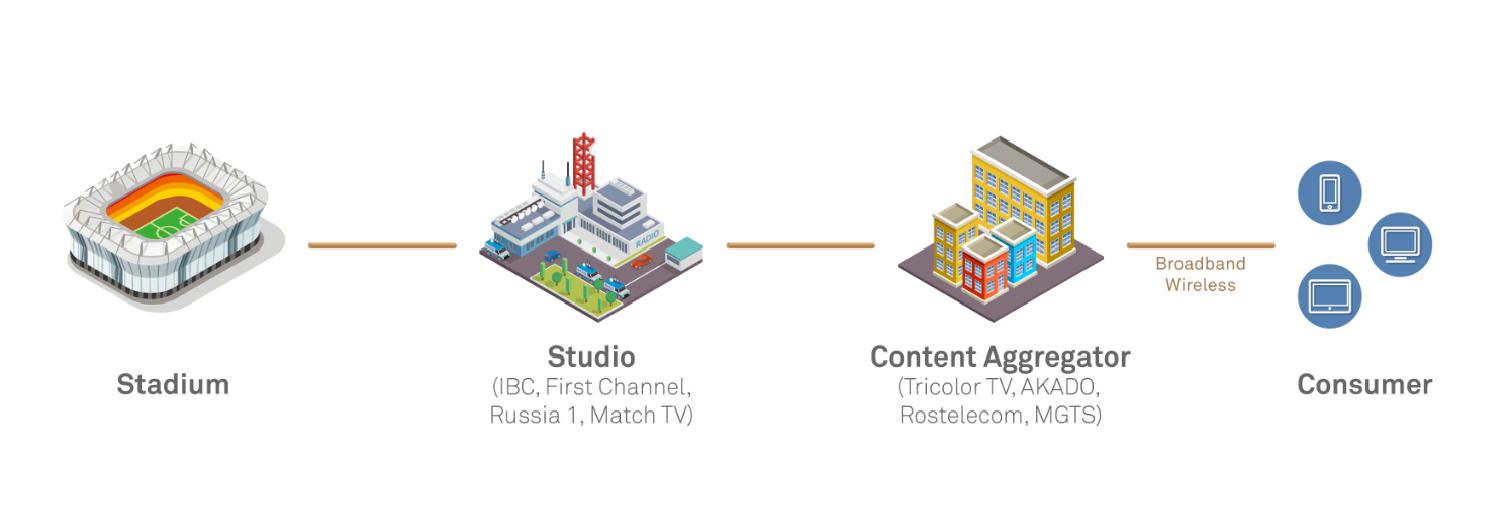
世界杯比赛俄罗斯本地的信号分发过程 俄罗斯世界杯每场比赛现场(共12座球场)采用了37个超高清UHD 4K HDR(15G的原生信号)摄像机位进行信号采集,与位于莫斯科的国际广播中心(IBC)进行通信,实现电视公用信号的制作和面向媒体的素材分发。俄罗斯本地获取转播权的电视台如First Channel、Russia 1和Match TV等获取公用信号和素材后各自进行后期制作(剪辑、配音合成、广告插播等)。 媒资信号的第一次分发叫:Contribution,分发的方向是由原始视频(直播, 节目摄影) 采集地(体育场馆、影视基地等)向制作中心;或原始视频在多制作中心之间分发,多分支协同制作。主要的玩家是电视台/直播公司,如BBC,IMG(英超联赛的制作公司)等。 而后电视台将制作完成的世界杯赛事节目分发给视频节目分销商,如俄罗斯的卫星广播运营商Tricolor TV、MSO运营商AKADO、电信运营商Rostelecom和MGTS进行节目内容聚合和分发。 此为媒资视音频信号的第二次分发叫:Primary Distribution,分发的方向是由制作中心(电视台,影视公司)向内容聚合和分销商(Cable TV/IP TV/ OTT/卫星等等)。主要的玩家是电视台,BBC,CNN, CCTV,SKY等。 视频分销商(Tricolor TV/AKADO/Rostelecom等)获取节目内容之后,进行视音频内容转码适配后分发给最终的用户。 这是媒资视音频信号的第三次分发叫:Secondary Distribution,分发的方向是由内容聚合和分销商向最终消费者。 由此可以看出媒资信号的第三次分发,主要由MSO运营商、电信运营商、卫星电视服务商、OTT等购买、聚合并交付内容给最终消费者,网络通常自建自用。 而媒资信号的第一、二次分发,围绕内容制作方---广播电视台为中心进行网络建设。广播电视台自身主要聚焦内容制作,分发网络通常采用租用和购买Services(专线/专网)的方式外包给第三方运营商进行建设和维护。 媒资业务的第一、二次分发,面向视频的生产方和分销商,传递媒体资产,就是运营商提供媒资专线/网的典型应用场景。 从摄像机到屏幕的视音频信号传播的分发过程,对承载网络的带宽、可靠性、时延、运维自动化等都提出了很高的要求,需要由专业服务商提供专线服务。 视频速率升级催生媒资专线换代 目前摄像机采集的数据通常以SDI信号输出,并以无压缩的方式透传原生视频内容到制作中心。主要原因是原始内容珍贵(视频的核心资产是内容),压缩之后就损失了后期制作的能力和价值。无压缩的原生视频内容也易于制作中心的IT系统简化和标准化。但这带来了传送数据量数十倍的增加,以及对整个承载网络带宽的巨大需求。 不仅如此,视频技术也在飞速发展,大众消费媒体资讯的方式和习惯也正悄然发生着改变。从标清SD到高清HD再到UHD(4K、8K)、360度全景VR,观众对画面清晰度的认识及要求(分辨率、帧频、颜色深度、声道上的提升)逐步提高。 SMPTE(美国电影与电视工程师学会)作为媒资广电行业的龙头组织,定义了相关的视音频信号标准。从表中可见从传统的SD-SDI到今日主流的HD/UHD,视频信号速率增长了10~40倍。
今天这些信号已由标清SD-SDI升级,带宽要求为1.5 Gbps 的HD-SDI(720p和1080i),以及使用3 Gbps的3G-SDI(1080p)成为主流。 4K / UHD摄像机(以12 Gbps或更高的速度运行)越来越多地被应用于市场,以提供更好的用户体验和享受。 广播电视公司也正在增加热门体育赛事/活动直播类节目的UHD化,使用更多摄像机和生成更多内容,视频/音频数量以及从场地传输的数据也一直在增加。以英超联赛为例,由运营商BT提供20个英超场馆到IMG工作室(Remote Production)的媒资专线,传输未压缩的实时HD高清直播信号。每场比赛提供20~34个(摄像机位,多角度立体拍摄)未压缩的高清视频信号(初始10~12路,2017年已达到24路:20路HD 1.5G信号,4路150M),总带宽已达30G,并要求支持分离路由的保护方式提高可靠性,从而每个场馆需要提供60G的带宽容量。 而且更多版权购买方对赛事信号提出了更高的质量需求,如Sky要求提供4K信号并计划使用VR直播英超,需要使用更高的网络速率进行扩容。 媒资SDI信号速率的升级以及更好用户体验的要求,带来媒资专线WAN互连端口的提速和容量的扩容,以及更高媒资专线SLA的要求,传统媒资专线需要更新换代。
媒资专线流量爆发式增长,发展前景巨大 媒资网是视频产业基础设施,每个国家均有媒资分发专线/网升级需求,潜在高价值客户分布广泛。从前端的内容采集回传制作中心,多分支的视频协同制作,到后端的视频内容分发给内容分销商播出,需要极致可靠的承载网,可参与市场空间巨大。 媒资客户分布广泛,蓝海市场空间巨大
提供媒资服务的专有Top电视台,仅西欧就有20+个国家电视台,通常会单独建设媒资专网,用于Outside Broadcasting视频数据,remote production信号回传,多facilities制作中心间WAN互联,音视频媒体数据中心互联和归档等。如
媒资专线通常合同期使用年限为5~10年,是长期稳定收入来源
媒资专线/网服务合同期长,通常为5~10年。运营商通常也会/可在合同中要求最低服务年限,譬如BT要求最低5年。此类专线网对服务提供商而言,是长期且稳定的收入来源。 运营商是媒资专线网的建设主体 电信运营商和MSO运营商都是媒资专线领域的主要玩家。 TOP电信运营商一直在为电视台和大型赛事活动提供媒资专线服务,如BT为BBC、ITV、英超提供专线/网,KPN为荷兰国家电视台提供专线/网等,成为行业标杆。 相比于电信运营商提供的专线网络,一些MSO运营商自身还具备内容制作能力,除了给自家电视台提供媒资专线服务之外,同时也在积极拓展媒资专线市场,为其他内容制作和生产方提供专线服务。
运营商提供媒资专线的样例 媒资专线分发网络通常采用租用和购买Services(专线/专网)的方式外包给第三方进行建设和维护。运营商在传输资源、网络/光纤覆盖/获取、带宽成本、网络管理经验上具备优势,是媒资专线分发网络的建设主体。运营商在媒资专网上的拓展主要可利用现有合同即将到期、媒资专线升级换代重新发标的时机,在解决方案差异化和整体成本上提升竞争力,积极投入媒资客户业务拓展,提供专线/专网服务。 华为正在携手德国运营商为国家级电视台建设基于OTN解决方案的媒资专线网络,提供超大带宽、低时延、高可靠、极简架构、敏捷灵活的新型媒资专线。 With the increasing demand of consumers for more content and higher video experience, the UHD of video program signal causes the rate upgrade, which promotes the upgrading of media-funded lines. As the infrastructure of video industry, media-funded private line has a wide distribution of potential high-value customers and is the new blue sea market for operators. Video and Audio Signal Propagation from Camera to Screen The 2018 Russian World Cup Football Match has brought a visual feast to the fans all over the world. Taking the local broadcast of this World Cup in Russia as an example, we will understand the distribution process of video and audio signals from camera lens material acquisition to end user screen. Local Signal Distribution Process in Russia during World Cup The Russian World Cup uses 37 UHD 4K HDR (15G original signal) camera bits for signal acquisition at each match (12 stadiums) to communicate with the International Broadcasting Center (IBC) in Moscow, so as to realize the production of public TV signals and the distribution of media-oriented materials. Local television stations in Russia, such as First Channel, Russia 1 and Match TV, acquire public signals and materials and then make post-production (editing, dubbing synthesis, advertisement insertion, etc.). The first distribution of media signals is called Contribution. The direction of distribution is from the original video (live broadcast, program photography) collection site (stadium, film and television base) to the production center; or the original video is distributed among multi-production centers, and multi-branch collaborative production. The main players are TV/live broadcasting companies, such as the BBC, IMG (the production company of the Premier League) and so on. Then the TV station will distribute the completed World Cup program to video distributors, such as Russian satellite broadcasting operator Tricolor TV, MSO operator AKADO, telecom operator Rostelecom and MGTS for content aggregation and distribution. This is the second distribution of media audio and video signals called Primary Distribution. The distribution direction is from production centers (TV stations, film and television companies) to content aggregators and distributors (Cable TV/IP TV/OTT/satellites, etc.). The main players are TV, BBC, CNN, CCTV, SKY and so on. Video distributors (Tricolor TV/AKADO/Rostelecom, etc.) acquire the content of the program, then transcode and adapt the video and audio content and distribute it to the final users. This is the third distribution of media audio and video signals, called Secondary Distribution, which is directed from content aggregators and distributors to end consumers. It can be seen from this that the third distribution of media signals is mainly purchased, aggregated and delivered to the final consumers by MSO operators, Telecom operators, satellite TV service providers, OTT, etc. The network is usually self-built and self-used. And the first and second distribution of media signals, around the content producer - Radio and television stations as the center for network construction. Radio and TV stations themselves focus on content production. Distribution networks are usually outsourced to third-party operators for construction and maintenance by leasing and purchasing services (private line/private network). The first and second distribution of media business, which is aimed at video producers and distributors, delivers media assets, is a typical application scenario for operators to provide media dedicated lines/networks. Distribution of video and audio signals from camera to screen requires high bandwidth, reliability, delay, operation and maintenance automation of the carrying network, which requires specialized service providers to provide dedicated line services. Video Rate Upgrading Promotes the Replacement of Media-funded Special Lines At present, the data collected by the camera is usually output by SDI signal and transmitted to the production center in an uncompressed way. The main reason is that the original content is precious (the core asset of video is content), and the ability and value of later production are lost after compression. Uncompressed native video content is also easy to simplify and standardize IT systems in production centers. However, this has led to a tens of times increase in the amount of data transmitted, as well as a huge demand for the bandwidth of the entire bearer network. Not only that, video technology is also developing rapidly, and the ways and habits of mass consumption media information are quietly changing. From SD to HD and then to UHD (4K, 8K) and 360-degree panoramic VR, the audience's understanding and requirements for picture clarity (resolution, frame frequency, color depth, channel improvement) have gradually improved. SMPTE (American Society of Film and Television Engineers), as the leading organization in the media-funded radio and television industry, defines the relevant video and audio signal standards. From the table, it can be seen that from traditional SD-SDI to today's mainstream HD/UHD, the video signal rate has increased by 10-40 times. Standard Name Bitrates Example video formats SMPTE 259M SD-SDI 270 Mbit/s 480i, 576i SMPTE 344M ED-SDI 540 Mbit/s 480p, 576p SMPTE 292M HD-SDI 1.485 Gbit/s 720p, 1080i SMPTE 372M Dual Link HD-SDI 2.970 Gbit/s 1080p60 SMPTE 424M 3G-SDI 2.970 Gbit/s 1080p60 SMPTE ST-2081 6G-SDI 6 Gbit/s 1080p120, 2160p30 SMPTE ST-2082 12G-SDI 12 Gbit/s 2160p60 SMPTE ST-2083 24G-SDI 24 Gbit/s 2160p120, 4320p30 Today, these signals have been upgraded by SD-SDI, with bandwidth requirements of 1.5 Gbps HD-SDI (720p and 1080i) and 3 Gbps 3G-SDI (1080p) becoming the mainstream. 4K/UHD cameras (running at 12 Gbps or higher) are increasingly being used in the market to provide better user experience and enjoyment. Broadcasting and television companies are also increasing the UHD of live sports events/events, using more cameras and generating more content, and the number of video/audio and data transmitted from venues has been increasing. Take the Premier League as an example. 华为智能高频开关电源华为高频开关电源,华为开关电源 |